Connect & track all your accounts
Sync and manage your financial info from 14,000+ financial institutions.
Customers for over 40 years
Best Mint Alternative
Best budgeting app
Best personal finance app
 Understand spending habits
Understand spending habits
 Manage subscriptions
Manage subscriptions
 Save more
Save more
 Pay down debt faster
Pay down debt faster
 Grow investments
Grow investments
 Improve net worth
Improve net worth
 Manage cashflow
Manage cashflow
 Get paid faster
Get paid faster
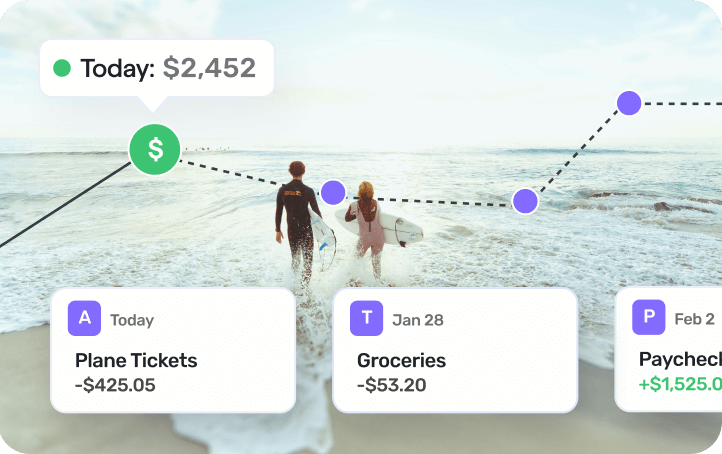
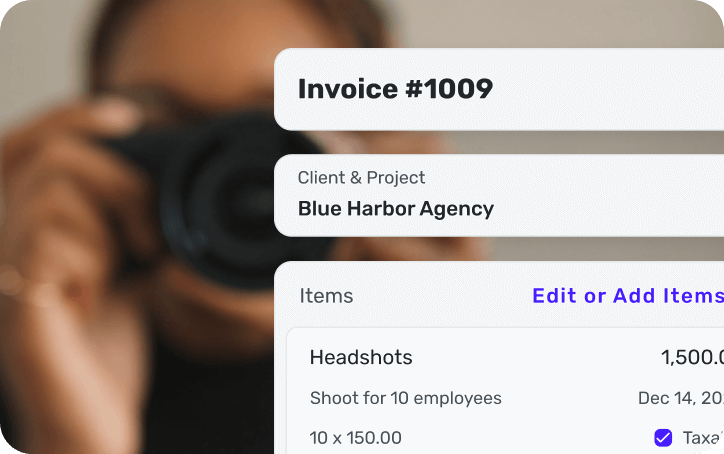



Connect & track all your accounts
Sync and manage your financial info from 14,000+ financial institutions.

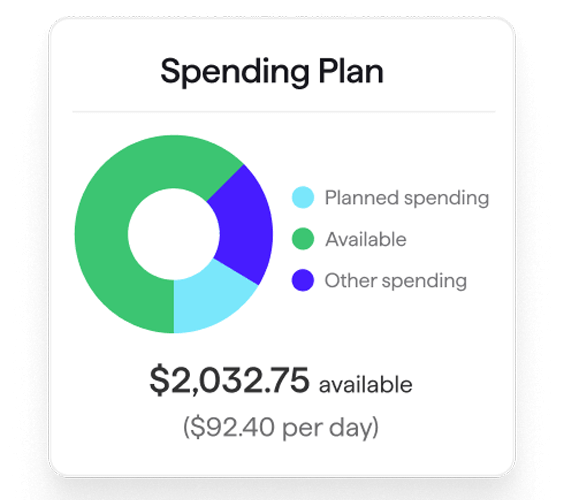
Spend & save with confidence
No matter your budget or savings goals, dial them in with Quicken
Tap 手机查询168官方开奖直播 insights you can act on
Generate future-focused reports and analyses for smarter decisions.

Build the future you want
Manage investments, retirement plans, and your entire portfolio.




168体彩站飞艇 Quicken

Quicken Business & Personal
Classic Premier
Classic Business & Personal

Trusted for over 40 years
#1 best-selling with 20+ million customers over 4 decades.

Bank-grade security
We protect your data with industry-standard 256-bit encryption.

Your privacy matters
Rest assured, we’ll never sell your personal data.

No surprise charges or ads
No hidden fees or annoying ads. What you see is what you get.




